Kubernetes Gateway API Inference Extension
By Daneyon Hansen (Solo.io), Kaushik Mitra (Google), Jiaxin Shan (Bytedance), Kellen Swain (Google) | Thursday, June 05, 2025
Modern generative AI and large language model (LLM) services create unique traffic-routing challenges on Kubernetes. Unlike typical short-lived, stateless web requests, LLM inference sessions are often long-running, resource-intensive, and partially stateful. For example, a single GPU-backed model server may keep multiple inference sessions active and maintain in-memory token caches.
Traditional load balancers focused on HTTP path or round-robin lack the specialized capabilities needed for these workloads. They also don’t account for model identity or request criticality (e.g., interactive chat vs. batch jobs). Organizations often patch together ad-hoc solutions, but a standardized approach is missing.
Gateway API Inference Extension
Gateway API Inference Extension was created to address this gap by building on the existing Gateway API, adding inference-specific routing capabilities while retaining the familiar model of Gateways and HTTPRoutes. By adding an inference extension to your existing gateway, you effectively transform it into an Inference Gateway, enabling you to self-host GenAI/LLMs with a “model-as-a-service” mindset.
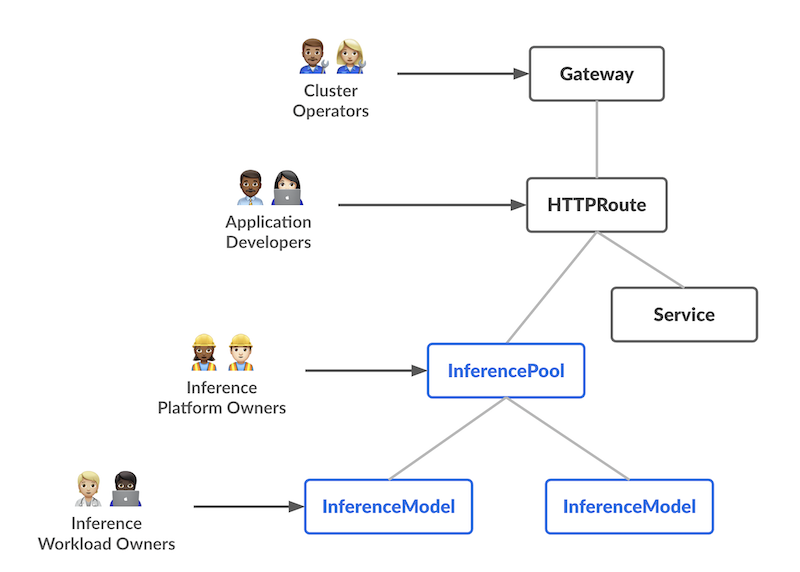
The project’s goal is to improve and standardize routing to inference workloads across the ecosystem. Key objectives include enabling model-aware routing, supporting per-request criticalities, facilitating safe model roll‑outs, and optimizing load balancing based on real‑time model metrics. By achieving these, the project aims to reduce latency and improve accelerator (GPU) utilization for AI workloads.
How it works
The design introduces two new Custom Resources (CRDs) with distinct responsibilities, each aligning with a specific user persona in the AI/ML serving workflow:
InferencePool
Defines a pool of pods (model servers) running on shared compute (e.g., GPU nodes). Platform admins configure deployment, scaling, and balancing policies. InferencePools are like Services but optimized for AI/ML workloads and support intelligent routing.
InferenceModel
Maps a public name (e.g., "gpt-4-chat") to an InferencePool, enabling traffic splitting, prioritization, and model version management.
Request flow
When a request is sent:
- The Gateway receives it—e.g. a POST to
/completions - Gateway resolves
InferencePoolvia HTTPRoute - An Endpoint Selection Extension (ESE) chooses the optimal Pod based on metrics
- Traffic is routed to that Pod, reducing latency and boosting resource usage
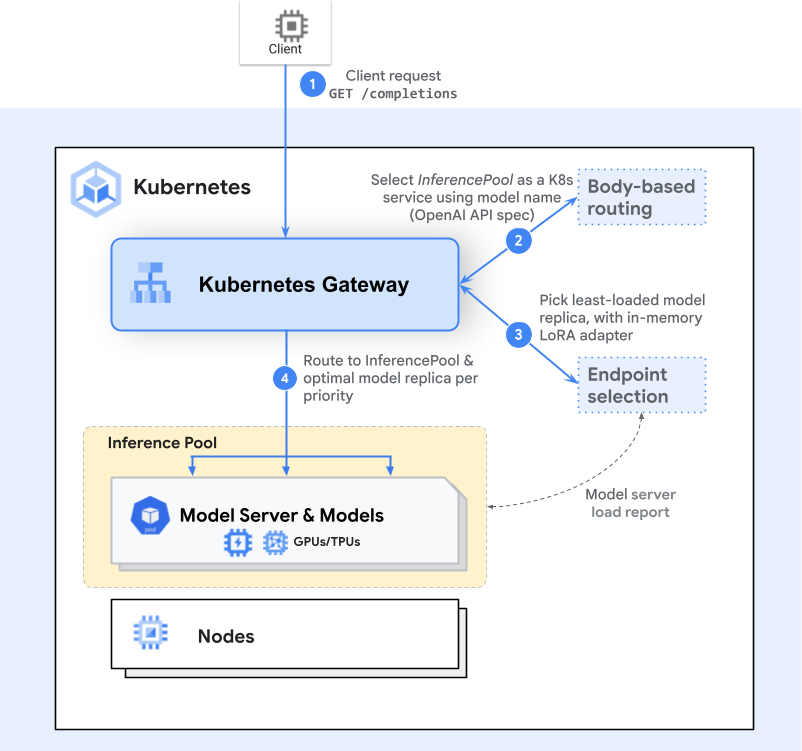
This adds inference-aware intelligence while maintaining standard Gateway API workflows.
Benchmarks
Testing with H100 GPU pods running vLLM (10 Llama2 models, 100–1000 QPS):
- Throughput stayed on par with standard Services
- p90 latency significantly dropped at high QPS (500+) thanks to smarter routing
Roadmap
Planned enhancements:
- Prefix-cache aware routing
- LoRA adapter rollout automation
- Workload fairness and autoscaling
- Support for heterogeneous accelerators and multi-modal inference
Summary
The Gateway API Inference Extension expands Kubernetes networking for GenAI workloads, adding model‑aware routing, priority, and smarter endpoint selection. It enables performance and scalability in AI-driven environments, making Kubernetes a better foundation for inference services.
Read the official docs and prototypes to get started.